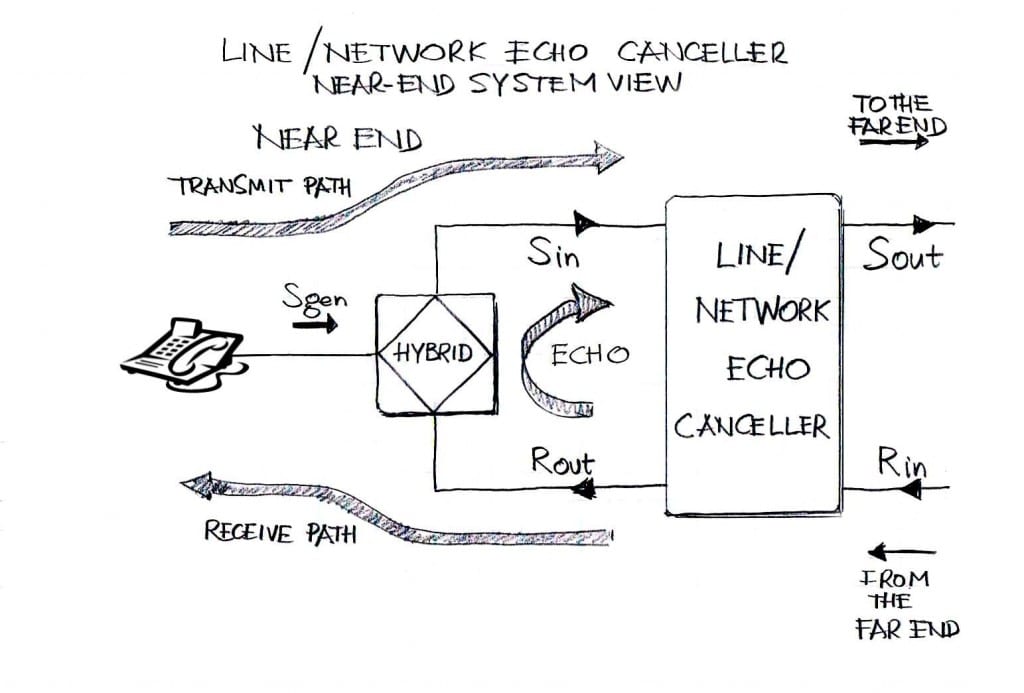
VOCAL’s Line/Network Echo Canceller is used in telecommunication applications to remove audible echoes caused primarily by electric signal reflections from the telephone hybrid circuit (a.k.a. telephone line transformer).
Telephone hybrid circuits convert 4-wire interface into 2-wire interface in POTS/PSTN systems. Historically, the introduction of the 4-wire-to-2-wire interface was motivated by the need to reduce the cost of copper loops connecting the POTS telephone line facility (access network) to individual subscribers. Figure 1 illustrates a typical line echo canceller operating at the near-end of the voice connection.
Signals travelling from the far end to the near end are reflected from the hybrid circuit, as a result of inadequate impedance matching between the telephone line and the hybrid terminals facing the telephone line. Although hybrid circuits are equipped with balance circuits that are selectable, ideal impedance matching can hardly be achieved due to line makeup/telephone set variations, which are not under telephone company control. These variations may occur even during the telephone call. Therefore, one of the requirements for the Line/Network Echo Canceller is that the adaptive filter, whose role is to rapidly identify the echo path (and specifically, the echo path impulse response), enters in the state of adaptation as soon as the voice channel between the near end and far end is open.
Typically the echo path impulse response of the hybrid circuit alone is relatively short and seldom exceeds 8-12 milliseconds. However, additional signal delays, due to signal paths linking the trunk facility and the line facility, have to be accommodated. This is why often Line/Network Echo Cancellers offer echo span coverage as large as 128 milliseconds.
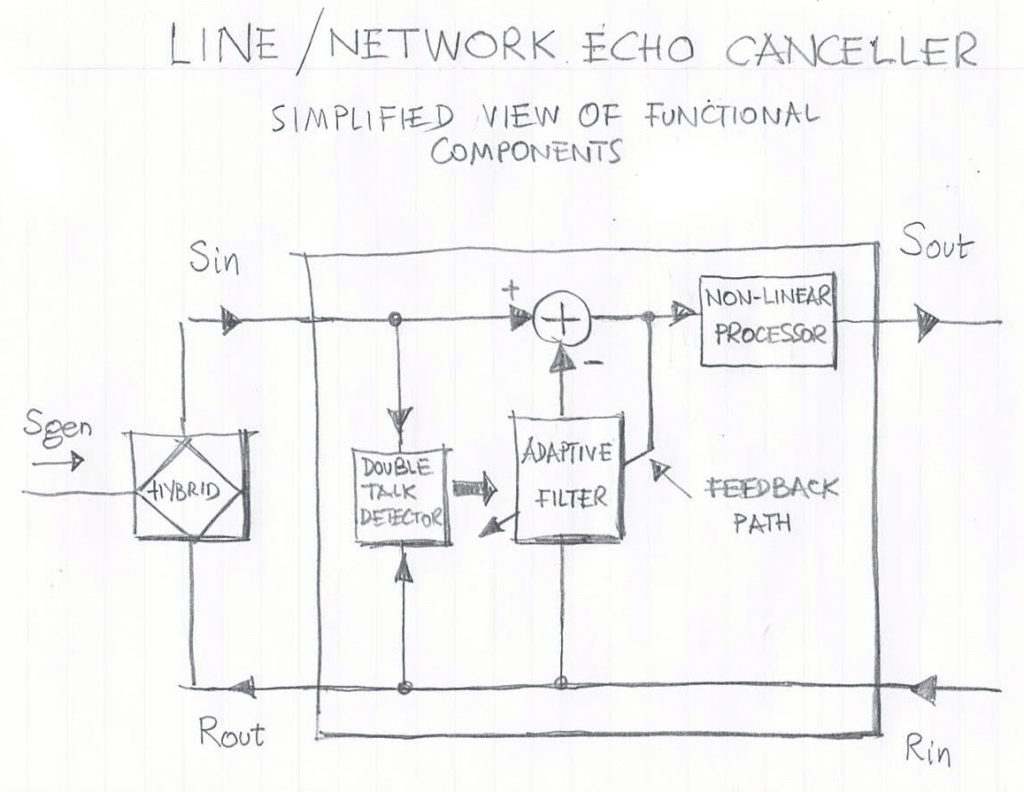
Typical building-blocks of Line/Network Echo Canceller are illustrated in Figure 2. The Adaptive Filter is one of the most important blocks. The internal structure of the adaptive filter as well as the adaptation algorithm are critical from the viewpoint of the echo canceller adaptation speed and depth characteristics. Double-talk detector block controls the adaption mechanism: if the near-end signal (Sgen) is present, the double talk halts the filter adaptation and thus prevents the filter from divergence. Nonlinear processor removes traces of residual echo from the error signal. The delay block (which often is optional) shifts in time the input signal to the adaptive filter in order to compensate signal delays between the echo canceller ports (Rout and Sin) and the ports of the line hybrid circuit.
VOCAL’s Line/Network Echo Canceller offers reconfigurable echo path coverage of up to 128 ms.
Features
- Fully compliant with ITU G.168-2015 Recommendations
- Rapid convergence and re-convergence ( for echo path changes)
- Double talk detection
- No divergence during double talk
- Adjustable echo tail length to 32 msec for full compliance
- Adjustable echo tail length to 128 msec with restricted compliance
- Proper operation during facsimile and low speed (<9.6 kbit/s) voice-band data transmissions
- Disables automatically in the presence of ANSam
- Excellent tone rejection and narrow band stability
- Non-linear processing (NLP) with Comfort Noise Generator (CNG)
- Tone detector and hold release logic
- Utilizes Normalized LMS (NLMS)
- Supports multiple channels
- Supports user callable functions
- Easily portable, re-entrant and re-locatable code